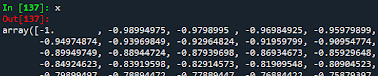
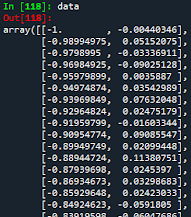
Introduction to Python!
We all have used calculators at university for math calculations, used GPS when we are located in an unknown place, asked our phone assistance to play some music from youtube, etc. But, do you know how all these wonderful things were created? Thanks to programming! Today, having knowledge of programming is very valuable no matter the background you have. It helps you better understand our today's technological world. There are several programming languages such as JavaScript, C++, Matlab, Python, and so on. All these languages use a similar syntax in terms of coding. If you have never heard about what programming is, or have heard about it, but never used any programming language before, I strongly recommend you to start with Python. Its simplicity will make you feel very comfortable and you will love coding. On this page, I will show you some interesting and useful applications in Python. In case you have no knowledge of programming, I suggest you to go through the beginne...